In today’s digital landscape, businesses face critical decisions about their IT infrastructure. Choosing between cloud computing and traditional hosting is a pivotal step, impacting scalability, cost-effectiveness, and overall performance. This article delves into the core differences between these two approaches, exploring the advantages and disadvantages of each to help you make an informed decision tailored to your specific needs. Understanding the nuances of cloud computing vs. traditional hosting is essential for maximizing your business’s potential in the modern technological era. We’ll examine key aspects like security, control, and maintenance to provide a comprehensive comparison of cloud vs. traditional hosting.
Whether you’re a burgeoning startup or an established enterprise, migrating to the cloud or maintaining a traditional hosting environment requires careful consideration. This guide will equip you with the necessary knowledge to differentiate between cloud computing and traditional hosting solutions. We’ll explore the core functionalities, pricing models, and potential challenges associated with each, empowering you to determine the optimal choice for your organization. From server management to data storage, we’ll analyze the key distinctions between these two prominent IT infrastructure paradigms, offering a clear understanding of cloud vs. traditional hosting in the context of your business objectives.
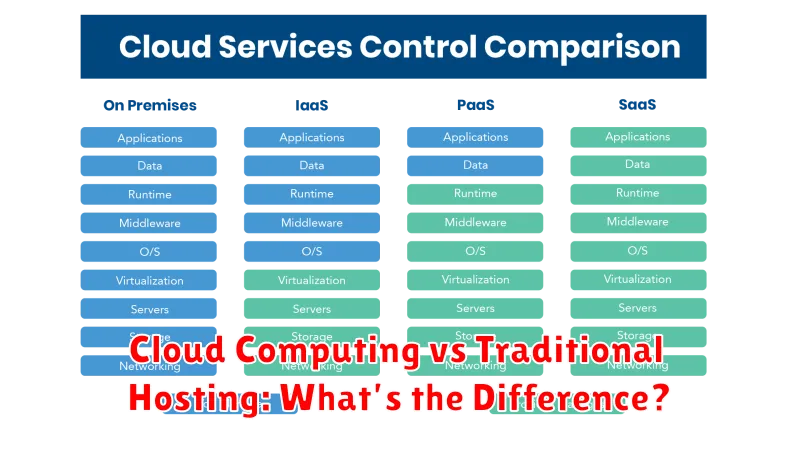
Defining Cloud vs On-Premise Hosting
Understanding the core difference between cloud and on-premise hosting is crucial. On-premise hosting, also known as traditional hosting, involves managing your own infrastructure. This means you are responsible for purchasing, maintaining, and securing all hardware and software within your own physical location.
In contrast, cloud hosting relies on a network of remote servers managed by a third-party provider. You essentially rent resources as needed, paying for what you use. This eliminates the need for upfront hardware investments and shifts the burden of maintenance and security to the provider.
Key Advantages of Cloud Infrastructure
Cloud infrastructure offers several key advantages over traditional hosting. Scalability is a primary benefit, allowing you to easily adjust resources based on demand, avoiding costly over-provisioning.
Cost-effectiveness is another advantage. You only pay for the resources consumed, eliminating upfront hardware investments and reducing ongoing maintenance expenses.
Increased reliability is achieved through redundancy and failover mechanisms built into cloud platforms. This ensures high availability and business continuity.
Enhanced security is offered by cloud providers who invest heavily in security measures and expertise, often exceeding what individual businesses can afford.
Performance and Scalability
A key difference between cloud computing and traditional hosting lies in performance and scalability. Traditional hosting relies on physical servers with fixed resources. This can lead to performance bottlenecks during peak demand. Upgrading requires manual intervention and often involves downtime.
Cloud computing offers significantly more flexibility. Resources can be scaled up or down automatically based on real-time needs. This elasticity ensures consistent performance even during traffic spikes. Furthermore, cloud providers often have multiple data centers, enabling redundancy and minimizing the impact of outages.
Cost Comparison Over Time
A key differentiator between cloud and traditional hosting lies in their cost structures over time. Traditional hosting often involves significant upfront investment in hardware, along with ongoing maintenance and upgrade costs. This creates a predictable, yet potentially higher, total cost of ownership over time.
Cloud computing, conversely, typically operates on a pay-as-you-go model. While there may be less initial capital expenditure, costs can fluctuate based on usage. Scalability is a key advantage of cloud, allowing businesses to adjust resources and costs according to demand, potentially leading to cost savings in the long run, particularly for businesses with variable workloads.
Comparing long-term costs requires careful consideration of factors like anticipated growth, usage patterns, and the specific pricing models of each provider. A thorough analysis is essential to determining the most cost-effective solution.
Security Considerations
Security is a critical aspect of both cloud computing and traditional hosting. With traditional hosting, you are responsible for the physical security and maintenance of your server. This includes implementing firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security measures.
Cloud providers, however, manage a significant portion of the security infrastructure. They typically have robust security protocols in place, including physical security of data centers and data encryption. However, you are still responsible for securing your applications and data within the cloud environment. Understanding the shared responsibility model is crucial in ensuring adequate security.
When to Choose Which Option
Deciding between cloud and traditional hosting depends on your specific needs. Cost is a key factor. Traditional hosting often involves upfront hardware investments, while cloud hosting operates on a pay-as-you-go model.
Scalability is another consideration. Cloud hosting offers easy scalability, allowing you to adjust resources as needed. Traditional hosting requires manual upgrades or downgrades.
Control and security also differentiate the two. Traditional hosting provides more direct control over your server environment, while cloud providers handle security infrastructure. Consider your technical expertise and security requirements when making your decision.