The metaverse represents a paradigm shift in how we interact with the digital world, transitioning from observers to active participants in a persistent, shared, and immersive 3D environment. This complete guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the metaverse, exploring its core components, including virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and blockchain technology. We will delve into the potential impact of the metaverse on various sectors, such as gaming, social interaction, commerce, and education, offering a clear picture of its transformative power. Understanding the metaverse is crucial for navigating the evolving digital landscape and harnessing its potential benefits.
This exploration will cover the key features of the metaverse, examining the creation of avatars, the development of virtual economies, and the role of decentralization. We will analyze the challenges and opportunities presented by the metaverse, addressing concerns about privacy, security, and accessibility. By the end of this complete guide, you will have a solid foundation for understanding the metaverse and its implications for the future of the internet and beyond.
What Is the Metaverse?
The metaverse is a network of interconnected, persistent, and immersive 3D virtual worlds. These worlds offer users diverse experiences, from gaming and socializing to commerce and education. It’s a convergence of physical and digital realities, blurring the lines between our online and offline lives.
A key characteristic of the metaverse is its interoperability. Ideally, users should be able to seamlessly transition between different virtual environments, taking their digital assets and identities with them. While this vision is still evolving, the metaverse represents a significant shift in how we interact with technology and each other.
Virtual Reality vs Augmented Reality
Both Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are integral technologies shaping the metaverse, but they offer distinct experiences. VR creates fully immersive, computer-generated environments, effectively transporting the user to a different world. This is achieved through devices like headsets that block out the real world.
AR, conversely, overlays digital information onto the real world. Users remain present in their physical surroundings while interactive digital elements, such as 3D models or text, are superimposed through devices like smartphones or specialized glasses. While VR replaces reality, AR enhances it.
Key Technologies Behind It
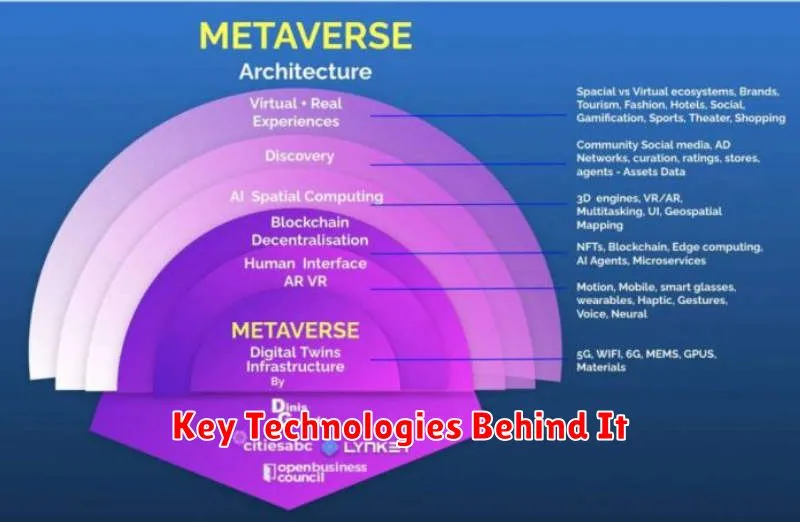
Several core technologies converge to create the metaverse experience. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are central, providing immersive visual and interactive experiences. AR overlays digital information onto the real world, while VR creates entirely simulated environments.
Blockchain technology offers secure and transparent digital asset ownership and management within the metaverse. This facilitates transactions and the creation of unique digital items. Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays a crucial role in powering realistic avatars, non-player characters (NPCs), and generating dynamic content. Finally, robust network infrastructure, including 5G and edge computing, is essential for supporting the low-latency and high-bandwidth requirements of a seamless metaverse experience.
How People Interact in Virtual Worlds
Interaction within virtual worlds hinges on several key elements. Avatars represent users, allowing them to express themselves and navigate the environment. Communication is facilitated through various means, including text chat, voice chat, and even gestures performed by avatars.
Shared experiences form the core of interaction. These can range from attending virtual events and playing games together to collaborating on projects and simply socializing. The level of immersion varies greatly depending on the platform and technology used, influencing how users perceive and interact with the virtual world and each other.
Concerns Over Privacy and Safety
The metaverse, while offering exciting possibilities, raises significant concerns regarding user privacy and safety. The immersive nature of these platforms necessitates the collection of vast amounts of personal data, including biometric information, location data, and even emotional responses.
This data collection raises questions about data security, potential misuse, and the lack of clear regulatory frameworks. The potential for cyberbullying, harassment, and identity theft within the metaverse are also critical concerns that require careful consideration and proactive solutions.
Furthermore, the psychological impact of prolonged immersion and the blurring lines between the virtual and physical worlds requires further study to ensure user well-being and safety.
Will It Replace the Web?
The metaverse is often touted as a potential successor to the web, but the reality is more nuanced. While the metaverse offers immersive and interactive experiences, it’s unlikely to fully replace the web as we know it.
The web excels at information dissemination and access to a vast repository of knowledge. The metaverse, on the other hand, focuses on creating shared, interactive experiences. Think of it less as a replacement and more as an evolution. The two are likely to coexist, with the metaverse offering new ways to interact with online content and connect with others.
Instead of replacing the web, the metaverse will likely augment it, providing new dimensions to online interaction and bridging the gap between the physical and digital worlds. The key difference lies in the level of immersion and the way users interact with the digital environment.

